- saxenadrsaurabh@gmail.com
- Sirmour Chauraha, LIC office ke Niche, Madhya Pradesh
- Mon - Fri: 8:00 am - 7:00 pm
- Home
- About Us
- Treatment’s
- Disorders Caused by Burns
- Long Non-Healing Wounds
- Skin Related Disorders
- Nasal Deformity Treatments
- Wounds & Scars on The Face
- Facial Bone Fractures
- Open Crush Injury
- Congenital Deformities
- Cleft Palate
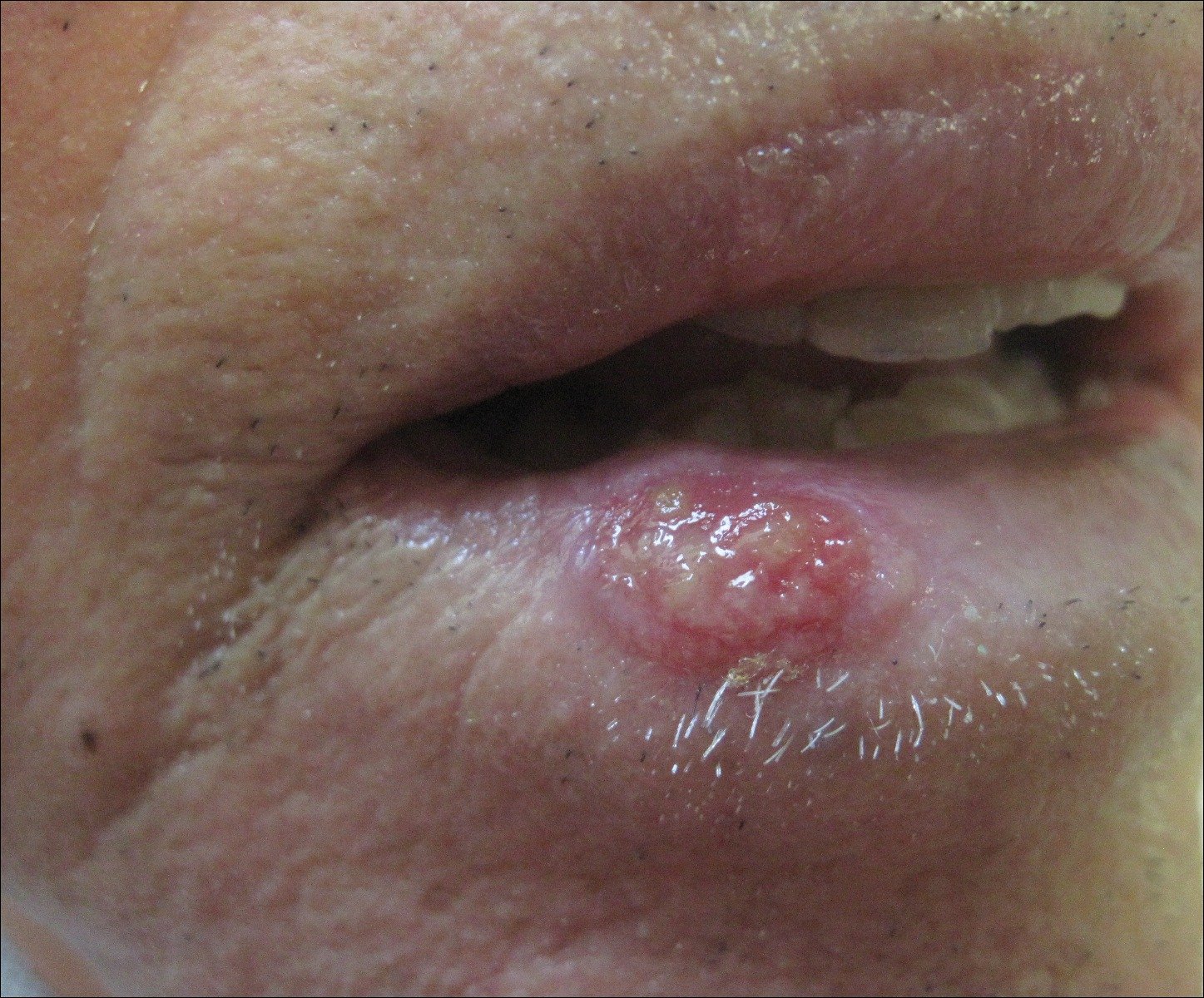
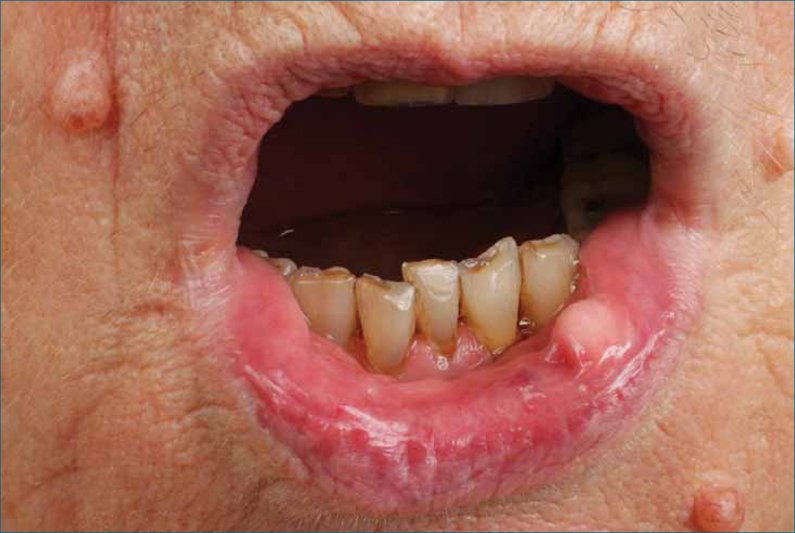
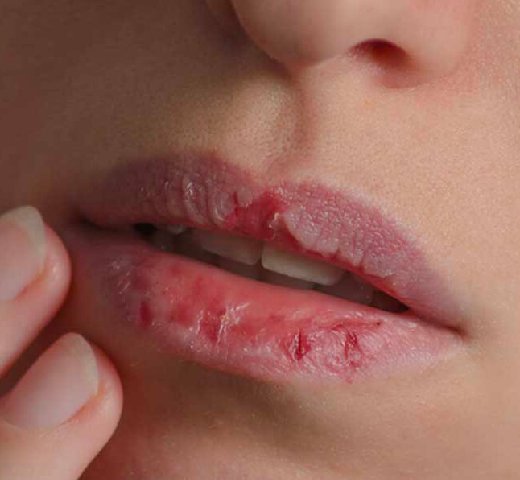
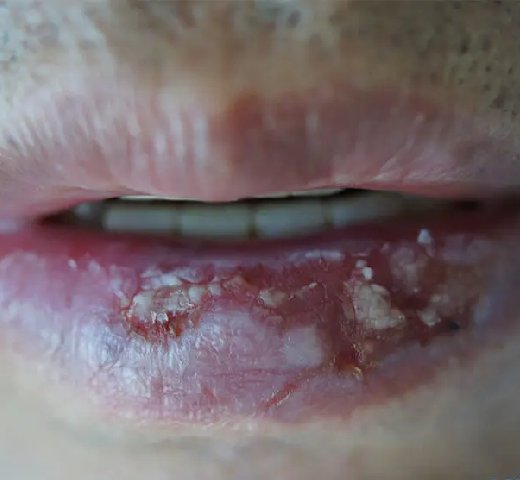
- BBC, SCC, LIP Cancer
- Hair Transplant Lipo Section
- Breast Reduction
- Breast Augmentation
- Tummy Tuck
- A-V fistula formation
- Laser Treatment
- Laser Surgery
- Hair Laser Removal
- PRP Therapy
- Insights
- Gallery
- News & Update
- Contact Us
Dr. Saurabh Saxena is a highly skilled dermatologist and cosmetic/plastic surgeon, specializing in surgeries and procedures aimed at enhancing appearance and restoring confidence.
Visiting Hours
| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
Gallery Posts